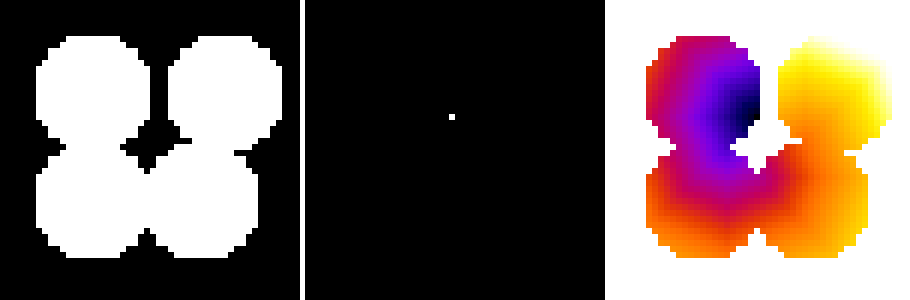
Seeded distance map¶
This example shows how to use the seeded distance map command. The example creates simple geometry consisting of four spheres, and calculates seeded distance map using an arbitrary point inside the top-left sphere as a seed point.
def seeded_distance_map():
"""
Demonstrates calculation of a seeded distance map.
"""
# Create geometry
geometry = pi.newimage(ImageDataType.UINT8, 50, 50, 50)
pi.sphere(geometry, [15, 15, 25], 10, 255)
pi.sphere(geometry, [15, 15 + 18, 25], 10.0, 255)
pi.sphere(geometry, [15 + 18, 15 + 18, 25], 10.0, 255)
pi.sphere(geometry, [15 + 22, 15, 25], 10.0, 255)
pi.writetif(geometry, output_file("sdmap_geometry"))
# Create seeds
seeds = pi.newlike(geometry)
pi.set(seeds, [24, 19, 25], 255)
pi.writetif(seeds, output_file("sdmap_seeds"))
# Calculate seeded distance map
sdmap = pi.newlike(geometry, ImageDataType.FLOAT32)
pi.sdmap(seeds, geometry, sdmap)
pi.writetif(sdmap, output_file("sdmap_result"))