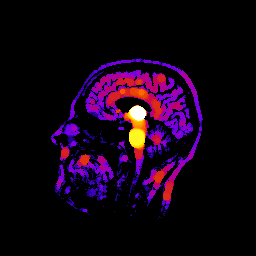
Local thickness / opening transform¶
This example demonstrates how to calculate local thickness map:
def thickmap():
"""
Demonstrates use of thickness map functions.
"""
# Read input image. Input must be binary (or it must be made binary,
# see e.g. 'threshold' command)
geom = pi.read(input_file_bin())
# Create output image
tmap = pi.newimage(ImageDataType.FLOAT32)
# Convert the input to large enough data type so that it can hold squared distance values.
# If the data type is too small, an error is raised.
pi.convert(geom, ImageDataType.UINT32)
pi.tmap(geom, tmap)
pi.writeraw(tmap, output_file('head_tmap'))
# If the default version consumes too much memory, there is also a slower memory-saver version.
# It is activated by setting last parameter of tmap to True:
geom2 = pi.read(input_file_bin())
tmap2 = pi.newimage(ImageDataType.FLOAT32)
pi.convert(geom2, ImageDataType.UINT32)
pi.tmap(geom2, tmap2, 0, True)
pi.writeraw(tmap, output_file('head_tmap_memsave'))