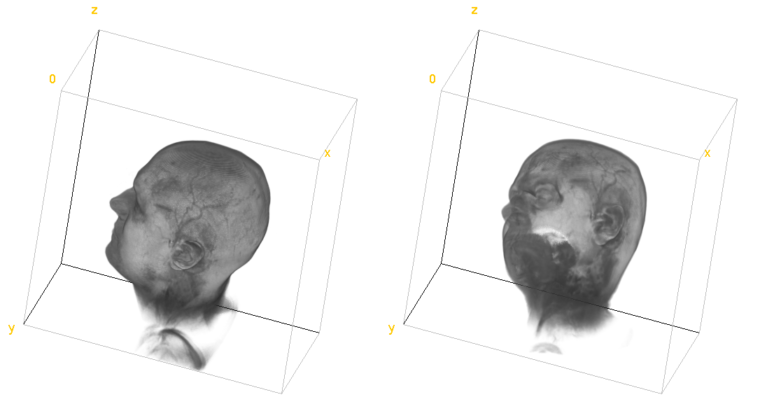
Image rotations¶
This example shows how to use rotate, rot90cw, rot90ccw, and reslice commands. First the example rotates input image 90 degrees clockwise, then 90 degrees around \(x\)-axis using the reslice command, and finally -60 degrees around vector \([1, 1, 0]\) using the rotate command.
def rotations():
"""
Demonstrates rotations and re-slicing.
"""
# Read image
img = pi.read(input_file())
# Rotate 90 degrees clockwise (around z-axis)
rot90 = pi.newimage()
pi.rot90cw(img, rot90)
pi.writetif(rot90, output_file('rotate_90_clockwise'))
# Reslice (rotate 90 degrees around x- or y-axis)
top = pi.newimage()
pi.reslice(img, top, ResliceDirection.TOP)
pi.writetif(top, output_file('reslice_top'))
# General rotation.
# NOTE:
# - The size of the output must be set to desired value before the call
# to rotate function.
# - The angle is given in radians. Here it is -60 degrees.
# - The axis is given as a vector and it does not need to be a unit vector.
grot = pi.newimage(img.get_data_type(), img.get_dimensions())
pi.rotate(img, grot, -60/180*3.14, [1, 1, 0])
pi.writetif(grot, output_file('general_rotation'))
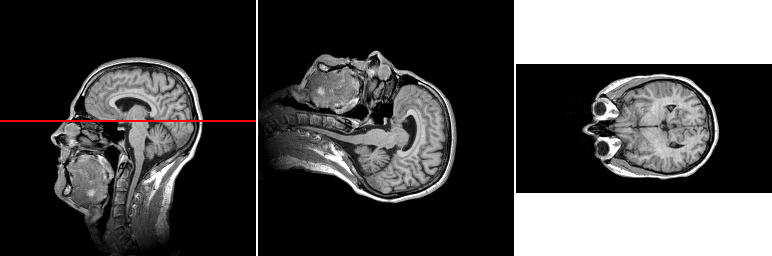
One slice of the input image (left), one slice of the input rotated 90 degrees clockwise (middle), and one slice of the input rotated 90 degrees around \(x\)-axis using the reslice command. The location of the slice in the rightmost panel is shown with red line in the leftmost panel.