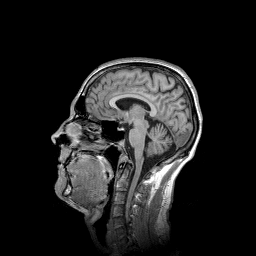
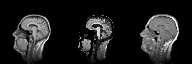
Binning¶
This example shows how to use different binning modes and what is their effect.
The default binning calculates average of each \((bin size)^3\) block of the input image, and makes that one pixel of the output image. The ‘min’ and ‘max’ modes take the minimum and maximum of the block, respectively, and make that value one pixel of the output image.
def binning_scaling():
"""
Demonstrates binning.
"""
# Read image
img = pi.read(input_file())
# Normal binning
binned_mean = pi.newlike(img)
pi.bin(img, binned_mean, 4)
pi.writeraw(binned_mean, output_file('binning_mean'))
# Min binning
binned_min = pi.newlike(img)
pi.bin(img, binned_min, 4, 'min')
pi.writeraw(binned_min, output_file('binning_min'))
# Max binning
binned_max = pi.newlike(img)
pi.bin(img, binned_max, 4, 'max')
pi.writeraw(binned_max, output_file('binning_max'))